Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hashimoto, Mie; Fukaya, Yuki; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Ichimiya, Ayahiko
Applied Surface Science, 254(23), p.7733 - 7736, 2008/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:17.12(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
 3-Pb studied by reflection high-energy positron diffraction
3-Pb studied by reflection high-energy positron diffractionFukaya, Yuki; Hashimoto, Mie; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Ichimiya, Ayahiko
Applied Surface Science, 254(23), p.7827 - 7830, 2008/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:17.12(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Kasukabe, Yoshitaka*; Nishida, Shinsaku*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Yoshikawa, Masahito; Fujino, Yutaka*
Applied Surface Science, 254(23), p.7942 - 7946, 2008/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:37.23(Chemistry, Physical)In order to clarify atomistic growth processes of TiN films due to ion implantation, in-situ observations by using transmission electron microscope and electron energy loss spectroscope at JAEA-Takasaki have been carried out, along with composition analysis and with the characterization of the electronic structure by molecular orbital calculation. The characterization of electronic structure of Ti films before and after implantation indicates that octahedral sites of hcp-Ti with larger space have higher electron density, which leads to the invasion of implanted ions into octahedral sites, and that the hcp-fcc transformation is induced by the shear in
films due to ion implantation, in-situ observations by using transmission electron microscope and electron energy loss spectroscope at JAEA-Takasaki have been carried out, along with composition analysis and with the characterization of the electronic structure by molecular orbital calculation. The characterization of electronic structure of Ti films before and after implantation indicates that octahedral sites of hcp-Ti with larger space have higher electron density, which leads to the invasion of implanted ions into octahedral sites, and that the hcp-fcc transformation is induced by the shear in  010
010 direction on (001) plane, promoted by the forming of
direction on (001) plane, promoted by the forming of  -type covalent bonds mainly consisted of hybridized orbitals due to combination of Ti3d and N2p, and by the weakening of Ti-Ti bonds.
-type covalent bonds mainly consisted of hybridized orbitals due to combination of Ti3d and N2p, and by the weakening of Ti-Ti bonds.
Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Ikeura, Hiromi*; Baba, Yuji
Applied Surface Science, 254(23), p.7812 - 7816, 2008/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Physical)We have constructed a novel rotatable time-of-flight (TOF) mass detector for desorbed fragment-ions produced by irradiation of synchrotron radiation (SR). This makes the best use of advantages in synchrotron, including variable X-ray energy, linear polarization, and pulsed capability. The detector allows us to measure excitation-energy dependences of desorbing ion yields from solid surfaces in a variety of incident angles of X-ray beams. We propose that this angle-dependent technique provides insights into orientation of chemical bonds lying at the top surface. The present paper reports our recent findings that the mass-patterns and yields of desorbed ions drastically depend on the incident angles less than 10 degrees. The results suggest that direct desorption mechanism prevails in extremely small angles and indirect desorption mechanism induced through collision excitation by secondary electrons is suppressed.
Tokura, Akio*; Maeda, Fumihiko*; Teraoka, Yuden; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Takagi, Daisuke*; Homma, Yoshikazu*; Watanabe, Yoshio*; Kobayashi, Yoshihiro*
no journal, ,
We have investigated the adsorption of atomic hydrogen on vertically aligned SWNT film. The effects of hydrogen adsorption were investigated by photoelectron spectroscopy and Raman spectroscopy. By fitting C 1s core level spectrum, we found the component attributed to hydrogenation of carbon. The suppression of  plasmons was also found. These results indicate that hydrogen adsorption induced bonding structure deformation. Raman spectra demonstrate that the radial-breathing-mode intensity of small-diameter SWNTs is more severely decreased than that of large-diameter SWNTs. The G-band/D-band ratio also decreased after the irradiation. These results indicate the disordering of graphene on small-diameter SWNTs is induced more easily. Our results indicate that the adsorption coefficient of hydrogen atoms for SWNTs with small diameter is higher than that for SWNTs with large diameter.
plasmons was also found. These results indicate that hydrogen adsorption induced bonding structure deformation. Raman spectra demonstrate that the radial-breathing-mode intensity of small-diameter SWNTs is more severely decreased than that of large-diameter SWNTs. The G-band/D-band ratio also decreased after the irradiation. These results indicate the disordering of graphene on small-diameter SWNTs is induced more easily. Our results indicate that the adsorption coefficient of hydrogen atoms for SWNTs with small diameter is higher than that for SWNTs with large diameter.
 7 at 300K
7 at 300KYoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden
no journal, ,
The time evolution of adsorption states was investigated by O1s and Si2p time-resolved XPS for oxidation of Si(111)-7 7 at 300K under the O
7 at 300K under the O ambient (5.3
ambient (5.3 10
10 Pa). Experiments were performed at SUREAC2000 of BL23SU in SPring-8. The O1s and Si2 XPS were measured alternatively by using synchrotron radiation (
Pa). Experiments were performed at SUREAC2000 of BL23SU in SPring-8. The O1s and Si2 XPS were measured alternatively by using synchrotron radiation ( 670eV,
670eV,  E
E 200meV). We succeeded in observation of the close correlation of each oxidation states during the oxidation. The initial rates of Si
200meV). We succeeded in observation of the close correlation of each oxidation states during the oxidation. The initial rates of Si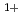 and ins is much larger than other components. Si
and ins is much larger than other components. Si and Si
and Si begin increasing around the dosage of the decrement of paul. The amount of paul is almost half of a maximum value at the decrease of Si
begin increasing around the dosage of the decrement of paul. The amount of paul is almost half of a maximum value at the decrease of Si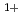 and after then the Si
and after then the Si clearly increases and the growth rates of Si
clearly increases and the growth rates of Si increases. The rates of decrement of Si
increases. The rates of decrement of Si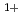 , increment of both Si
, increment of both Si and insx2-ad become loose after the disappearance of paul. The Si
and insx2-ad become loose after the disappearance of paul. The Si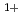 decreases at increasing insx2-ad again.
decreases at increasing insx2-ad again.
 adsorption and dissociation on the electrode in the electrolysis
adsorption and dissociation on the electrode in the electrolysisSuzuki, Chikashi; Nakagiri, Toshio
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shimoyama, Iwao; Li, X.*; Shimada, Takashi*
no journal, ,
It has been reported that single-walled carbon-nanotubes (SWNTs) align on several single crystal surfaces with chemical vapor deposition. In order to investigate the alignment mechanism, we measured polarization-dependent Raman spectra of aligned SWNTs formed on quartz single crystal surfaces. High- and low-frequency components in tangential vibration modes of Raman spectra, i.e., G (
( 1590cm
1590cm ) and G
) and G bands (
bands ( 1575cm
1575cm ), exhibited different magnitudes of polarization dependence. High-frequency G
), exhibited different magnitudes of polarization dependence. High-frequency G band always showed larger polarization dependence than low-frequency G
band always showed larger polarization dependence than low-frequency G band independently of polarization configuration, resonant excitation condition, and growth condition. Base on these results, we concluded that different polarization dependences between G
band independently of polarization configuration, resonant excitation condition, and growth condition. Base on these results, we concluded that different polarization dependences between G and G
and G bands originated from different orientations of semiconducting and metallic SWNTs. This suggests that semiconducting SWNTs selectively align on quartz crystal surfaces.
bands originated from different orientations of semiconducting and metallic SWNTs. This suggests that semiconducting SWNTs selectively align on quartz crystal surfaces.
Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Baba, Yuji; Shimoyama, Iwao; Hirao, Norie*; Nath, K. G.*; Uddin, M. N.*
no journal, ,
We have constructed a novel rotatable time-of-flight (TOF) mass detector for desorbed fragment-ions produced by irradiation of synchrotron radiation (SR). This makes the best use of advantages in synchrotron, including variable X-ray energy, linear polarization, and pulsed capability. The detector allows us to measure excitation-energy dependences of desorbing ion yields from solid surfaces in a variety of incident angles of X-ray beams. We propose that this angle-dependent technique provides insights into orientation of chemical bonds lying at the top surface. The present paper reports our recent findings that the mass-patterns and yields of desorbed ions drastically depend on the incident angles less than 10 degrees. The results suggest that direct desorption mechanism prevails in extremely small angles and indirect desorption mechanism induced through collision excitation by secondary electrons is suppressed.
 /Si(001) interface studied by XPS using synchrotron radiation
/Si(001) interface studied by XPS using synchrotron radiationOgawa, Shuichi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Ishizuka, Shinji*; Teraoka, Yuden; Takakuwa, Yuji*
no journal, ,
In this study, to investigate the oxidation-induced strain accumulating during the first oxide layer growth on Si(001) surface, two oxidation reaction modes of the first oxide layer, Langmuir-type adsorption and two-dimensional oxide island growth at 573 K and 923 K, respectively, were comparatively investigated by real-time XPS at the BL23SU of SPring-8. The experimental results obtained suggest that the oxidation-induced strain is smaller at 923 K than at 573 K.